Toyota’s financial performance has taken a hit, with the company reporting its first quarterly revenue decline in nearly three years. d hybrid investments.
Toyota announced a significant decline in its operating revenue for the first half of fiscal year 2025, reporting a total of approximately $16 billion (¥2.64 trillion).
Toyota’s operating revenue declined by 20% during the second quarter, totaling approximately $7.55 billion (1.16 trillion yen), marking its first quarterly revenue decline in two years.
The decline in income is primarily attributed to the downturn in automotive sales, which was caused by certification issues leading Toyota to temporarily halt production of its popular Yaris Cross and Corolla Fielder models in Japan. A Prius recall in the US, coupled with reduced global inventory, resulted in fewer vehicles being offered internationally.
For the first time in four years, Toyota’s global production declined in the first half of fiscal 2025. Toyota manufactured 4.71 million vehicles, a 7% decline from the previous year’s record 5.06 million units.
Toyota’s domestic production declined by 9.4% and international manufacturing decreased by 6%. Chinese markets proved particularly challenging for international automakers, as companies like BYD continued to aggressively displace them with affordable and increasingly competitive electric vehicles.
Toyota will continue investing in electric vehicle (EV) technology until the very end?
Although Toyota initially forecast a rebound in manufacturing by the end of its fiscal year, it now expects a total output of 9.4 million vehicles for the year, a 1% decrease from last year’s total.
Toyota’s Vice Chairman Yoichi Miyazaki revealed strategies for sustaining revenue while simultaneously investing in the company’s long-term growth and development.

Toyota will delay decisions on hybrid, plug-in hybrid, battery electric, and fuel cell electric vehicle technologies until the very last moment, according to Miyazaki. The corporation plans to closely track market trends before making a decision.
Meanwhile, the corporation is continuously pushing forward with innovative technological advancements, including the development of superior electric vehicle (EV) batteries. Toyota’s vice chairman has officially revealed that the company is actively developing its own electric vehicle battery technology, with a focus on three distinct types: ternary, lithium-iron phosphate (LFP), and all-solid-state variants.
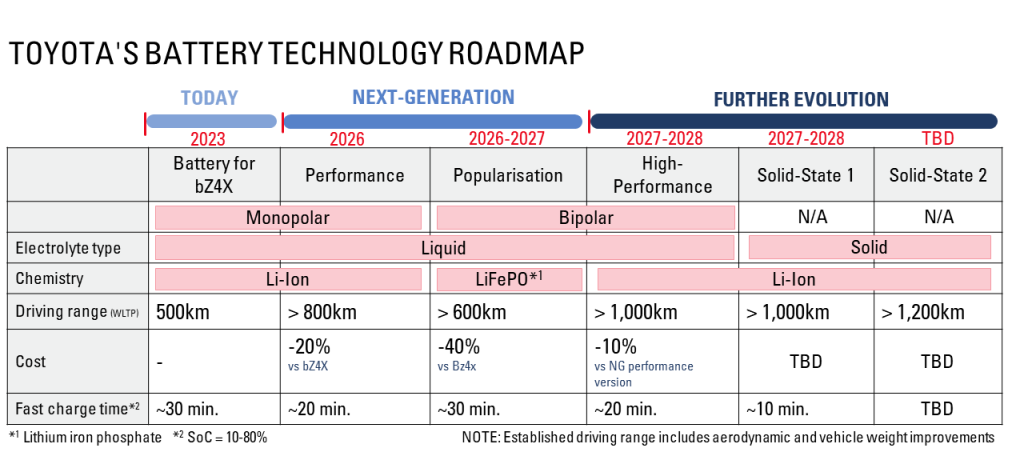
In March, Toyota transformed its battery business into a fully owned subsidiary by converting the Toyota Battery unit into a standalone entity. The corporation stated that the transfer facilitates “optimal timing” and is crucial for large-scale production of various battery types.
Miyazaki clarified that there were two key challenges that needed to be addressed: Our mission is to significantly accelerate our response time to environmental shifts in an era where predicting the long-term future has become increasingly challenging. Additionally, we aim to strengthen our fundamental capacities, enabling us to thrive and adapt for generations to come?











