Toyota plans to build a state-of-the-art electric vehicle battery factory on Japan’s “Silicon Island”, a move aimed at keeping pace with Chinese competitors like BYD and other emerging players in the electric car market? Toyota’s new manufacturing unit aims to bolster its electric vehicle supply chain by producing batteries for its high-end Lexus models.
Although Toyota has historically trailed other manufacturers in the transition to electric vehicles, the company now acknowledges the need to keep pace with rapidly advancing Chinese electric vehicle (EV) makers such as BYD.
Following the debut of its initial electric vehicle, the Atto 3, in Japan, BYD is now poised to roll out three EVs onto Toyota’s home territory. China’s BYD unveiled its much-anticipated Tesla Model 3 rival, the Seal EV, last month, priced from ¥5.28 million, equivalent to approximately $33,100 on the market.
According to the Japan Car Importers Association (JAIA), in the first half of 2024, Chinese electric vehicle imports comprised nearly 10% of all vehicles shipped into Japan during this period.
Accessing the Japanese market requires a deliberate strategy to navigate its complexities. Japanese automakers such as Toyota lead the country’s domestic market, while imported vehicles tend to be luxury brands from Europe, including BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Porsche.
Following a remarkable surge of 184%, passenger car imports to BYD skyrocketed in the past year, driven primarily by the Chinese automaker’s expansion strategy.
Toyota is countering BYD’s surge by establishing a new EV battery plant on Japan’s southernmost island of Kyushu, which will be its fourth such facility.
Toyota to build a state-of-the-art electric vehicle (EV) battery production facility in Japan.
According to plans, Toyota’s battery manufacturing subsidiary, Primearth EV Technology, will operate the new facility.
The island, a hub for automotive and semiconductor industries, earns the moniker “Silicon Island.” Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Co., Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), the world’s leading independent semiconductor foundry and a key player in the global technology supply chain, has officially launched its second fabrication facility on the island of Taiwan.

Toyota’s new plant will help strengthen its export capabilities to Asia and solidify its electric vehicle supply chain. Located approximately 25 miles (40 km) from Toyota’s Miyata plant, the facility primarily manufactures Lexus vehicles for international markets.
According to the report, the capability will serve as the primary enabler of its Miyata facility’s success. The plant boasts an impressive annual capacity of approximately 430,000 units, with a staggering 90% of its production being exported globally.

As the market shifts towards Asia, Toyota aims to safeguard its position. Chinese EV manufacturers, including BYD, are expanding their reach across Asia by offering competitive, budget-friendly electric vehicles.
Toyota constructs batteries near its Miyata plant to avoid unnecessary transportation costs and save valuable time?
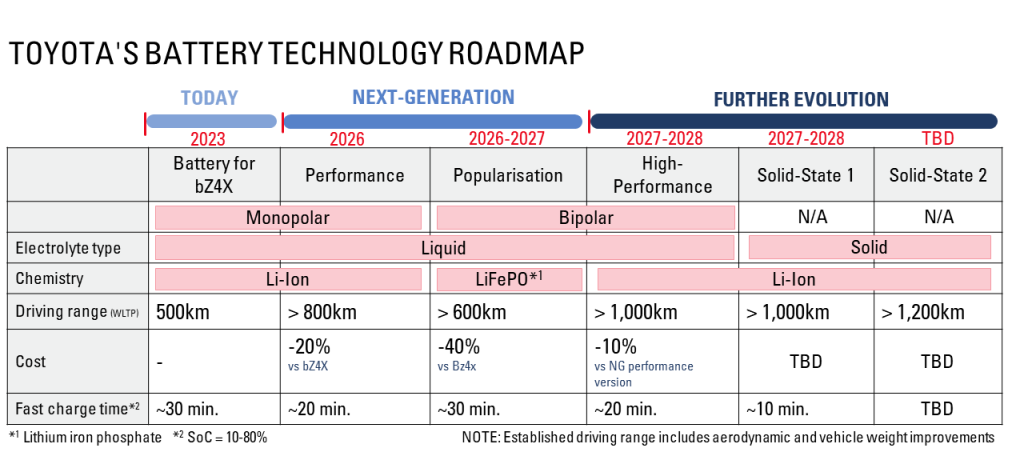
The corporation intends to invest approximately $32 billion (5 trillion Japanese yen) in electric vehicles (EVs) by 2030, with a significant portion dedicated to battery development and production. By that time, Toyota aims to boost annual electric vehicle sales to approximately 3.5 million units. In its final 12 months, the company acquired a total of 104,000 units.
Toyota has yet to reveal the budget for its newly announced EV battery plant or provide a timeline for the project’s commencement, although further details are expected shortly. What’s the exact story on this situation?











